Simultaneous analysis of an elastomer spring joint for applied operational loads
Sector: Rail vehicle constructionSpecialist field: Structural mechanicsThe elastomer spring joint is one of the energy-absorbing elements in the couplings of rail vehicles. CADFEM used simulation tools from Ansys to determine the stresses in the spring joint shell as well as in the bearing pedestal for Voith Turbo in order to further optimize the elastomer spring joint.
Summary
Task
For the spring joint being analyzed, it was necessary to determine the stresses that occur in the surrounding shell as well as in the coupling when the elastomer spring elements are supported on the shells under the various forms of loading.
Solution
Calculations with high deformations still represent a challenge for implicit FE simulation today. Further hurdles for numerical analysis result from the nonlinear material behavior of rubber. With the element approaches provided by Ansys, CADFEM was able to meet the high demands on numerical calculations for incompressible material behavior.
Customer benefits
Based on the calculation results of CADFEM in Ansys, the shell and coupling geometry could be optimized.
Project Details
Task
For the spring joint being analyzed, it was necessary to determine the stresses that occur in the surrounding shell as well as in the coupling when the elastomer spring elements are supported on the shells under the various forms of loading. The operating loads generate high shear forces, which lead to large deformations of the elastomers.
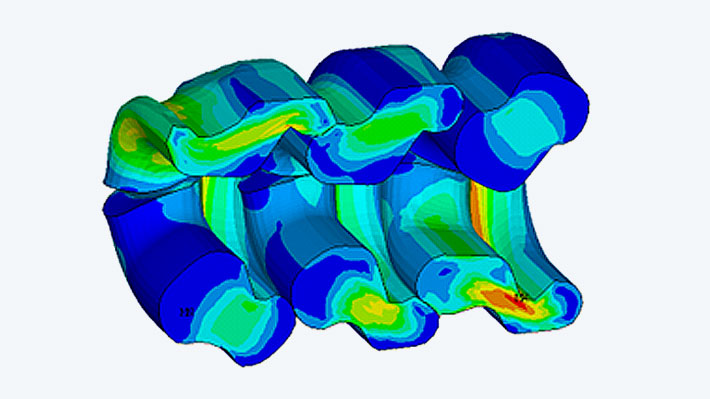
Customer Benefit
Based on the calculation results of CADFEM in Ansys, the shell and coupling geometry could be optimized.
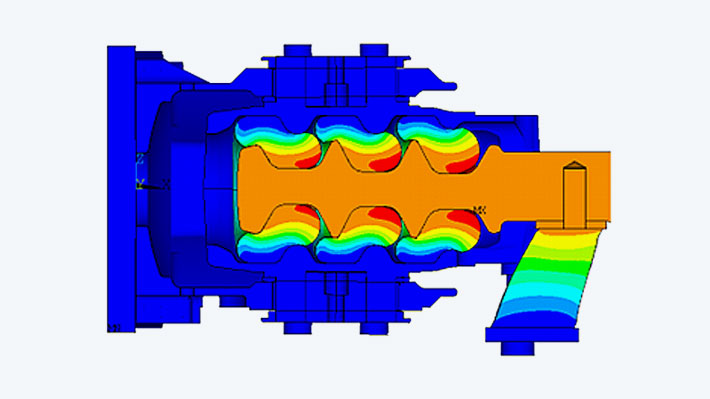
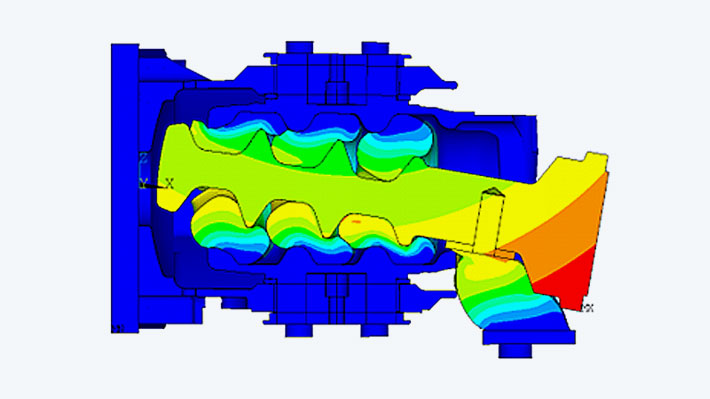
Solution
Calculations with high deformations are a challenge for implicit FE simulation until today. Further hurdles for the numerics arise from the nonlinear material behavior of rubber, its almost complete incompressibility and the nonlinear contacts included in the model .Structural mechanics analysis of an elastomer-spring joint.
In the present case, the customer provided results from push-pull tests of the elastomer spring elements. These data were used to adjust the parameters for the rubber material law used in the simulation. The element approaches provided by Ansys were chosen in order to take into account the high numerical requirements resulting from the nearly incompressible material behavior of the rubber and the large deformations.
Images: © Voith Turbo




