
Using ANSYS to analyze nickel/Incoloy weld seams on a rocket engine
Sector: AerospaceSpecialist field: Structural mechanicsIt is required that a nozzle casing joint on the engine of the Ariane 5 rocket be welded. The seam combines galvanized nickel with Incoloy through the use of an electron-beam weld.
Summary
Task
The metallurgical properties for the areas in which the initial welds and the final welds overlap needed to be calculated. Root penetration also had to be simulated. In addition, process variants needed to be investigated.
Solution
CADFEM used ASNYS Mechanical to generate a finite element model for the sector containing both the initial and the final areas of the weld seam. This was followed by calculation of the transient temperature field and a mechanical stress analysis involving plastic material behavior.
Customer benefits
The user obtained notes that enabled them to single-handedly investigate different approaches to controlling the welding process.
Project Details
Task
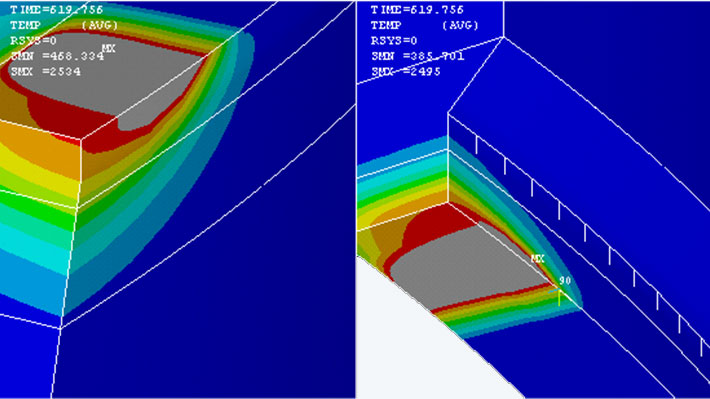
It is required that a nozzle casing joint on the engine of the Ariane 5 rocket be welded. The seam combines galvanized nickel with Incoloy through use of an electron-beam weld. The seam follows a radial path. The areas of the initial weld and the final weld will overlap. It was necessary to calculate the metallurgical properties for these areas and to simulate root penetration. Process variants also needed to be investigated.
Customer Benefit
Notes were created for the user that enabled them to single-handedly investigate different approaches to controlling the welding process.

Solution
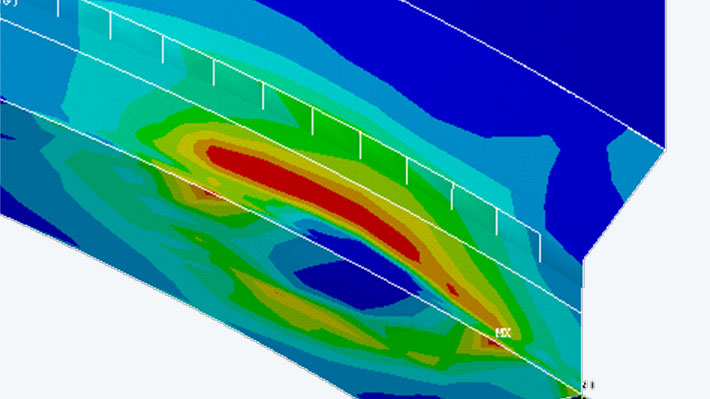
The finite element model was generated for the sector containing both the initial and the final areas of the weld seam. The first step in the calculation was to calculate the transient temperature field, with the electron beam being represented by a surrogate heat source. A mechanical stress analysis involving plastic material behavior was then performed. At the gap in the seam, the joining of the sides of the seam was idealized using a temperature-dependent joint.
Images: © ariane group




